What is the Difference between 2D and 3D Rotary Laser Tube Cutting
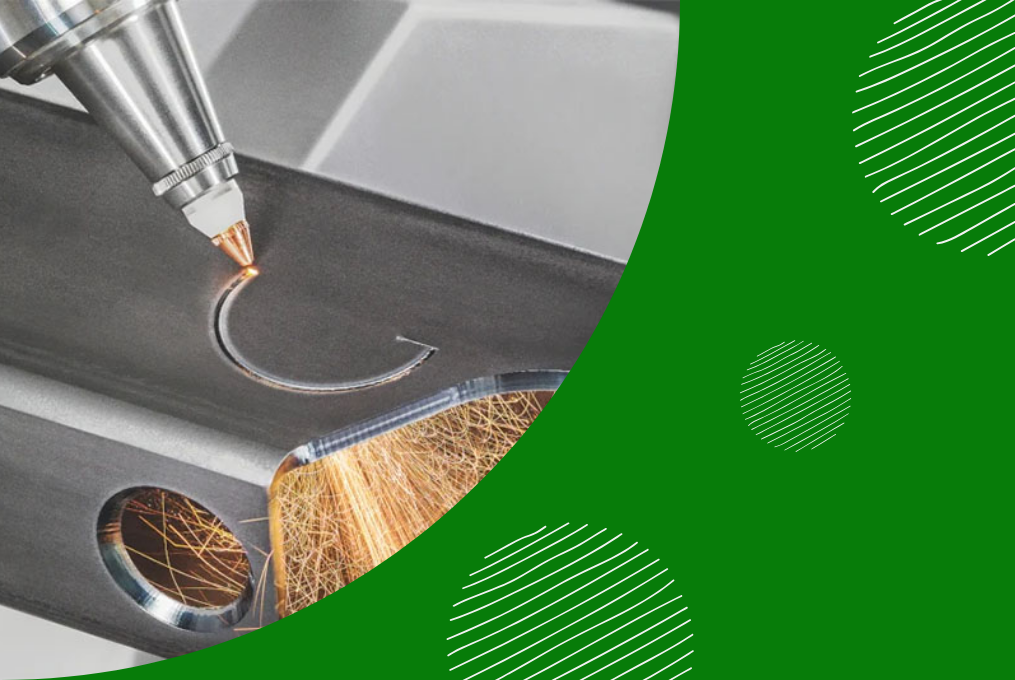

If you're in the world of manufacturing or fabrication, you've probably come across laser cutting. It's a popular technique used for cutting through materials like metal, plastic, or wood. But did you know that there are different types of lasers cutting? When it comes to cutting tubes and pipes, two of the most common methods are 2D rotary laser tube cutting and 3D rotary laser tube cutting. While both are highly effective, they have key differences. In this blog, we’ll break down what sets them apart, how they work, and where they are best used.
Understanding 2D Rotary Laser Tube Cutting
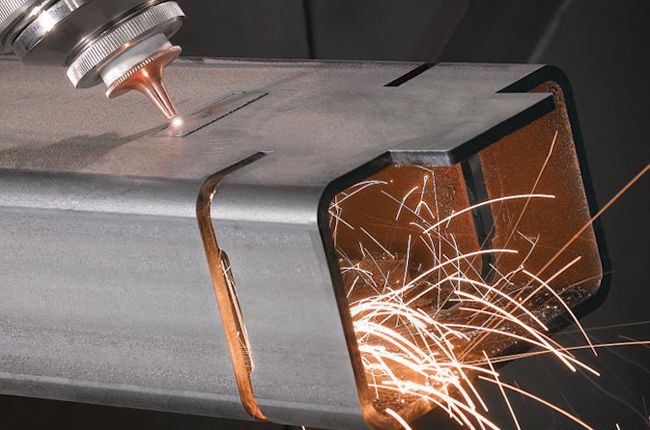

Let’s start with the basics. 2D rotary laser tube cutting is the process of cutting through a material, like a metal tube or pipe, using a laser that works in two dimensions. The “2D” part means that the laser is cutting along a flat plane, usually from top to bottom or side to side.
In simple terms, think of it like cutting through a pipe in straight lines or simple curves. The pipe or tube stays in place or rotates, and the laser makes the cuts from one side.
How It Works
The process involves a high-powered laser beam that melt, burns, or vaporizes the material. The tube rotates, but the laser only cuts in a flat, 2D direction. This works well for designs or cuts that are more basic and don’t require complex angles.
When to Use 2D Laser Tube Cutting
2D laser cutting is perfect for:
Basic shapes: If you need straight cuts or simple curves.
Mass production: It’s faster and more efficient for producing large quantities.
Simple designs: Ideal when you don't need detailed, multi-angle cuts.
For example, if you're cutting a large number of tubes for a basic frame or structure, 2D rotary laser cutting might be the best option. It gets the job done quickly and efficiently.
Understanding 3D Rotary Laser Tube Cutting
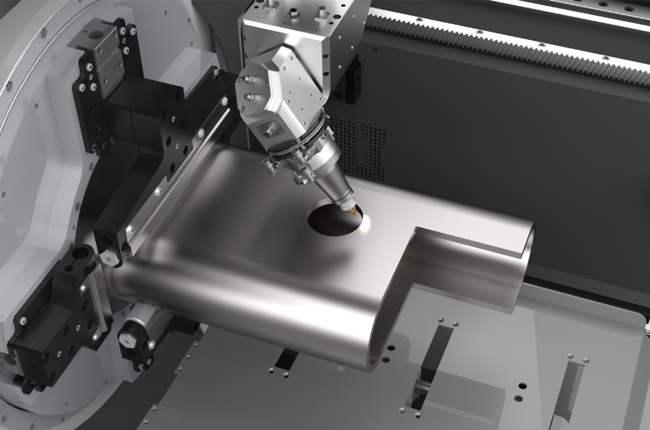
Now, let’s move to 3D rotary laser tube cutting. Just like the name suggests, this method allows you to cut tubes and pipes into three dimensions. The laser here can move in more complex ways—cutting not just in straight lines, but also at angles, curves, and more intricate shapes.
Imagine you want to cut a tube that has different cutouts on multiple sides or angles. In this case, 3D rotary laser cutting is the go-to technique.
How It Works
In 3D cutting, the laser head can tilt and rotate, allowing for cuts from multiple angles. The tube rotates, but now the laser can cut in more than just a flat plane. It can move up, down, and side to side, creating detailed and complex designs.
When to Use 3D Laser Tube Cutting
3D laser tube cutting is ideal for:
Complex designs: If your project requires intricate cuts or angled holes.
Custom fabrication: When you need detailed, custom-made pieces.
Prototyping: 3D cutting is perfect for creating unique prototypes or small production runs.
For example, in industries like aerospace or automotive manufacturing, where tubes and pipes need to fit together perfectly at odd angles or shapes, 3D rotary laser cutting is the preferred choice.
Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Rotary Laser Tube Cutting
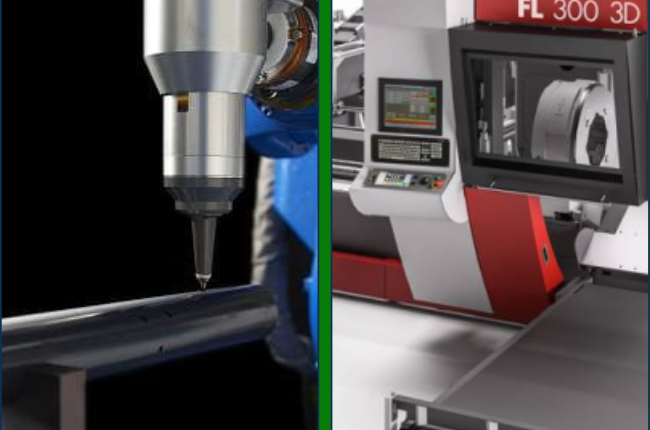

Now that we understand the basics of each process, let’s look at the key differences between 2D and 3D rotary laser tube cutting:
Cutting Directions:
a. 2D laser cutting works in a flat, two-dimensional plane. The cuts are made in simple straight lines or curves.
b. 3D laser cutting allows the laser to move in multiple directions, creating more complex, angled, or multi-sided cuts.
Complexity of Designs:
a. 2D cutting is great for basic designs and high-speed production.
b. 3D cutting is better suited for more intricate designs that require precision from various angles.
Flexibility:
a. 2D cutting is limited in terms of the shapes it can create.
b. 3D cutting is much more flexible, allowing for more creative designs and custom fabrication.
Cost and Time:
a. 2D cutting is generally faster and more cost-effective when working with simple shapes.
b. 3D cutting takes more time and can be more expensive, but it’s worth it for projects that require high precision.
Applications:
a. 2D rotary laser tube cutting is often used in industries where high-speed, simple designs are needed, such as construction or furniture manufacturing.
b. 3D rotary laser tube cutting is more common in industries like aerospace, automotive, and other fields that require complex, custom parts.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between 2D and 3D rotary laser tube cutting depends on your project’s needs. If you’re looking for speed and efficiency with simple designs, 2D cutting is probably your best bet. On the other hand, if your project requires precision, custom cuts, and multi-dimensional designs, 3D cutting is the way to go.
In short:
Choose 2D for fast, simple cuts and high-volume production.
Choose 3D for more complex, detailed designs that need accuracy and flexibility.
Both methods are effective, but they shine in different situations. Knowing the difference can help you make the right decision for your next project!
Wrapping Up!
Understanding the difference between 2D and 3D rotary laser tube cutting can help you choose the right technique for your specific needs. Whether you’re working on simple structures or detailed, custom projects, both methods offer powerful ways to get the job done.