What is Design for Manufacturing and Assembly?

Design for Manufacturing and Assembly, or DFMA, is a design approach that helps companies create products that are easier, faster, and more cost-effective to produce. In simpler terms, DFMA is about making products in a way that simplifies the manufacturing process, reduces costs, and ensures high quality. Let’s break down what DFMA is, why it matters, and how it can benefit companies, designers, and customers alike.
Breaking Down DFMA: Two Key Parts
DFMA is made up of two essential concepts:
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Design for Assembly (DFA)
Let’s look at each one separately to understand how they work together.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
DFM focuses on creating products that are easy and cost-effective to manufacture. This part of DFMA considers how a product’s design will impact the manufacturing process. For example, choosing the right materials, selecting the best manufacturing techniques, and thinking about how each component will be made.
By optimizing a product for manufacturing, companies can reduce costs by eliminating waste, cutting down production time, and using materials more efficiently. DFM aims to streamline the manufacturing process as much as possible, allowing the company to produce high-quality products quickly and at a lower cost.
Design for Assembly (DFA)
DFA, on the other hand, is all about making sure that products are easy to assemble. It considers how different parts will fit together and how quickly the product can be assembled. A product that is easier to assemble means it takes less time, reduces the chances of errors, and lowers labor costs.
For example, if a product has fewer parts or uses standardized parts, it’s typically easier to assemble. Reducing the number of steps required for assembly makes the process smoother, faster, and less expensive. DFA focuses on ensuring that assembly workers or automated machines can put the product together with ease.
Why DFMA Matters
DFMA has become an essential practice for many companies, especially in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. But why is it so important?
Cost Savings
By making products easier to manufacture and assemble, companies can save a lot of money. Using DFMA, they can avoid unnecessary design complexity, reduce waste, and minimize the need for costly manufacturing processes. Cost savings make a big difference, especially when producing large volumes.
Improved Quality
Simpler designs often lead to fewer errors. When a product is easy to make and assemble, there’s less chance for mistakes, meaning higher quality for the customer. DFMA can help create products that are more durable and reliable.
Faster Production Times
Products designed with DFMA principles can be manufactured and assembled faster. This speed can be especially important in industries with tight deadlines or high demand, like consumer electronics.
Environmental Impact
DFMA can also help reduce a product’s environmental impact. With simpler designs, there’s less waste in production, and manufacturers can choose materials that are more eco-friendly. Efficient assembly processes can also reduce energy consumption and emissions.
Key Principles of DFMA
Let’s look at some of the basic principles that guide DFMA. Following these principles helps companies design products that are both easy to produce and assemble.
Minimize Parts
Reducing the number of parts in a product makes it easier to assemble, saves material costs, and simplifies the manufacturing process. If a part does not add a specific function or value, it may be best to leave it out.
Use Standard Components
Using standardized parts or components that are commonly available can save time and money. It can also make maintenance or repairs easier since standard parts are easier to replace.
Choose Easy-to-Handle Materials
Using materials that are easy to cut, mold, or shape can simplify the manufacturing process. For example, choosing materials that can withstand machining or molding processes well can speed up production.
Simplify Assembly Directions
Making sure that parts only fit together in one way can make assembly easier and reduce the risk of mistakes. Design parts in a way that clearly shows how they should fit with other parts.
Optimize for Automated Processes
With the rise of automation, designing products that can be easily assembled by machines is a key part of DFMA. Simple designs with fewer moving parts are often more compatible with automated manufacturing.
Benefits of DFMA for Businesses and Consumers
DFMA offers benefits for everyone involved in the production and use of a product:
For Manufacturers: DFMA reduces production costs, speeds up manufacturing, and makes assembly more efficient. It also helps companies stay competitive by delivering high-quality products at lower costs.
For Designers: By adopting DFMA principles, designers can make better choices early in the design phase. This approach not only reduces revisions but also results in more functional, high-quality products.
For Customers: The benefits of DFMA extend to customers as well. Products designed with DFMA principles are often more reliable and cost-effective. Additionally, these products tend to be more eco-friendly due to reduced material waste and streamlined manufacturing.
Real-World Examples of DFMA
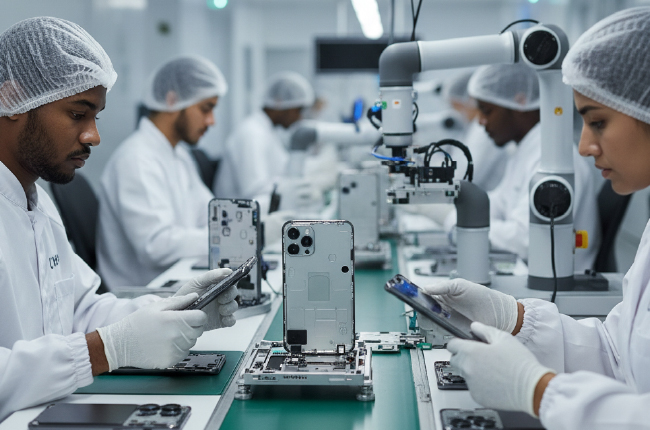

Let’s look at some real-world applications of DFMA:
Smartphone Manufacturing
Many smartphone companies use DFMA principles to create phones that are easier to assemble. For example, using fewer screws and relying on snap-fit parts can make assembly quicker and easier.
Automobile Industry
In the automotive world, DFMA is applied to design car parts that are easier to manufacture and assemble. Car manufacturers reduce the number of components in engines and other parts to save assembly time and reduce costs.
Wrapping Up!
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) is about making products that are easier and cheaper to produce while maintaining high quality. It helps businesses save money, reduce production times, and deliver reliable products to customers.
By following DFMA principles, companies can create products that are simpler, more efficient, and often more environmentally friendly. This approach benefits everyone—designers, manufacturers, and customers alike—making it a powerful tool for modern manufacturing.