Understanding Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in Product Design

In today's environmentally conscious world, knowing a product's environmental impacts is very important when designing eco-friendly products. So, here comes the role of life cycle assessment, where the environmental impacts of a product are measured and accessed through a life cycle. The life cycle assessment of a product is a complete structure that determines the product's opportunities and improvement. We can say just in one word: "Life cycle assessment and sustainability can be an effective strategy to innovate, optimise, and minimise impact, rolling the way for a greener future." In this blog, the reader will learn a few things about LCA, the 4 stages of life cycle assessment, its definition, and its application to sustainability. Let's explore here: -
What is Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)?
Before going more on this topic let’s first know the life cycle assessment definition: - Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is an approach to evaluating the environmental aspects of a product, process, or service throughout its life cycle.
Life cycle assessment methodology for products designs includes: -
Raw Material Extraction
Manufacturing
Distribution
Usage
End-Of-Life Disposal or Recycling
When a product's life cycle analysis passes through these stages, it helps with energy consumption, resource depletion, and waste generation.
Why is LCA Important in Product Design?
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is very important for a sustainable product design; the reasons behind: -
LCA helps designers focus on using eco-friendly materials and processes.
Governments and industries often require LCA for environmental reporting.
Sustainable practices improve a company's reputation and build customer trust.
Using resources efficiently with LCA can save money in production and logistics.
The Four Phases of LCA
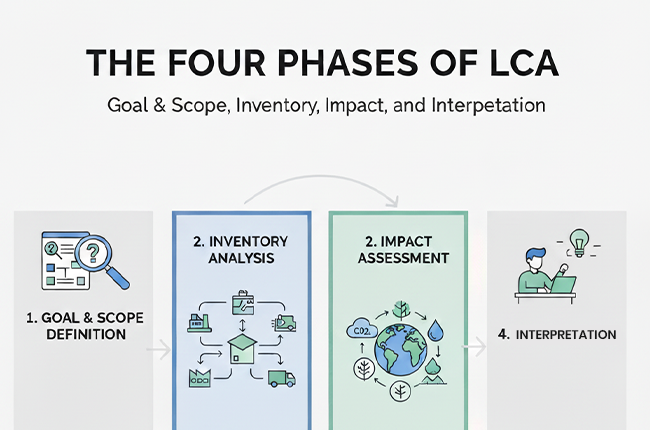
The Life cycle assessment stages are widely divided into four phases, which include: -
1 Goal and Scope Definition: Here, those who conduct LCA for their products must define the objectives of the LCA study and the boundaries of the assessment. Like
What is the purpose of the LCA?
Which processes and systems will be included?
2 Inventory Analysis: In this phase, diagramming is done for the product through LCA by collecting data on material inputs, energy usage, emissions, and waste generation.
3 Impact Assessment: The third stage of a product's Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) includes assessing the environmental impacts linked to the inventory data, such as carbon footprint, water usage, and potential toxicity.
4 Interpretation: The final stage includes analysing all the findings collected from product design, manufacturing processes, or materials that help to make informed decisions.
Applications of LCA in Product Design
The life cycle assessment companies use life Cycle Assessment (LCA) – The systematic processes in the following areas: -
Material Selection: This method is used to identify low-impact, recyclable, or renewable materials.
Eco-Design: Using this life cycle assessment, one can create products with minimal environmental impact.
Packaging Solutions: Adding one more benefit - It reduces waste by optimising packaging design.
Circular Economy Models: Using this LCA, resources can be reused, recycled, and remanufactured instead of discarded.
Tools and Methodologies for Conducting LCA
The life cycle assessment companies make use of a few tools: -
SimaPro
GaBi
OpenLCA
TRACI
Using these tools can facilitate data collection, maintain accuracy, and provide detailed information on environmental impacts, making LCA more efficient and accessible.
Challenges in Implementing LCA
When life cycle assessment companies make use of these LCA, they face a few hurdles such as: -
Sometimes, collecting appropriate data for each stage of the product's life cycle becomes more difficult.
One conducting LCA with poor knowledge can face challenges while understanding various processes requiring expertise.
The first stage of LCA can be expensive, so smaller businesses tend to avoid this process.
Lack of time when gathering data across the entire product life cycle.
Many companies and designers still need to familiarise themselves with LCA, limiting its widespread adoption and effective implementation.
The Future of LCA in Sustainable Design

There is a saying, "Necessity is the mother of invention", and so we can get a chance to see more invention and growth to build a sustainable world. A few emerging innovations are: -
Integration with AI and Big Data
Dynamic LCA Models
Circular Economy Integration
Blockchain for Transparency
Final Thoughts
The blog will surely give you a deeper understanding of life cycle assessment and how one can use it in different ways. An effective LCA for your products can help you maximise environmental efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability throughout the product life cycle.
Adopting LCA for your product design can help you build a sustainable world, improve your brand's reputation, and meet the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.