Generative Design: The Future of Engineering
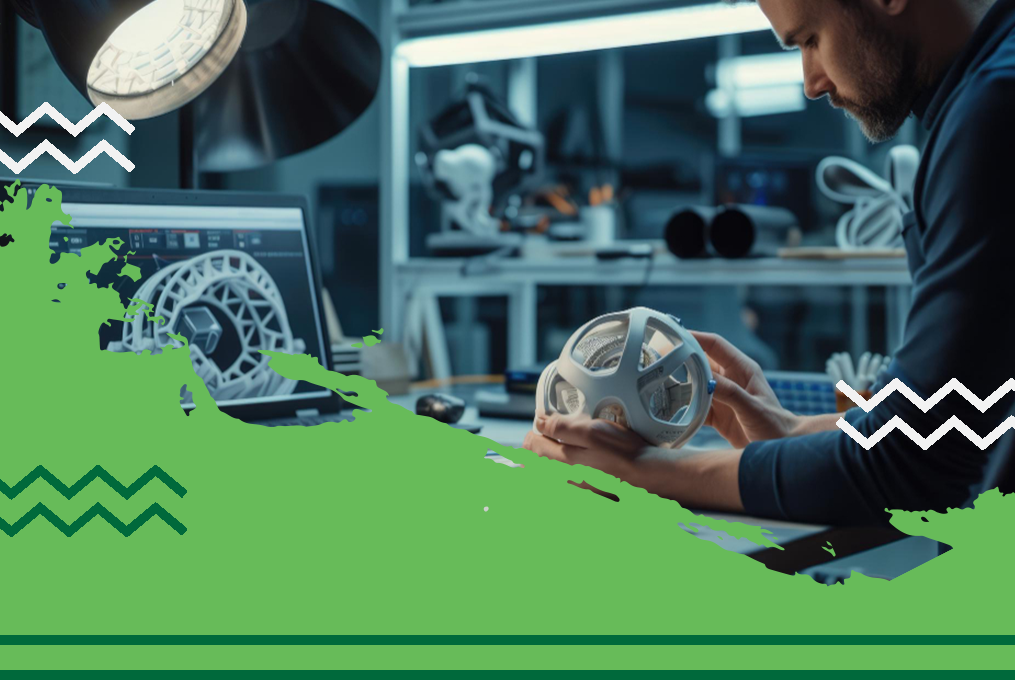

Imagine if engineers and designers had a tool that could create thousands of design options in minutes, learning and evolving with each design choice. This tool isn’t just a dream; it’s a reality, thanks to generative design. As technology advances, generative design is fast becoming the future of engineering, helping companies worldwide to innovate faster, make products stronger, and reduce costs. Let’s dive into what generative design is, how it works, and why it’s changing the way we approach engineering.
What is Generative Design?
In simple terms, generative design is a computer-aided process that allows engineers to explore many design possibilities by inputting specific goals and constraints. Engineers and designers give the software certain requirements—like weight, strength, cost, materials, or manufacturing methods. The software then generates a wide variety of potential designs that meet these conditions, sometimes offering thousands of options.
These options aren’t random. The software uses advanced algorithms, often powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to learn from each design iteration. This way, each new design generated is a bit better or closer to what the designer is looking for. It’s like giving a team of digital designers a challenge and letting them work together to come up with the best solutions.
How Does Generative Design Work?
The process starts with engineers setting design goals and constraints. This might include:
Material choice – Will the object be made of steel, aluminum, plastic, or another material?
Weight limits – If designing aerospace, for example, weight is a critical factor.
Strength and durability – How strong do the product need to be? What pressures or forces will it need to withstand?
Cost – Engineers can set a budget to ensure the design options are financially practical.
Manufacturing methods – The design might need to be 3D printable, molded, machined, or even handcrafted.
After setting these parameters, the generative design software creates hundreds, if not thousands, of designs that fit these requirements. Engineers can then review and pick the best options, often tweaking the design further or repeating the process until the best solution emerges.
The designs generated might even be ones that humans would never think of on their own, featuring unique shapes and structures that optimize strength, weight, and material usage.
Why is Generative Design Important?
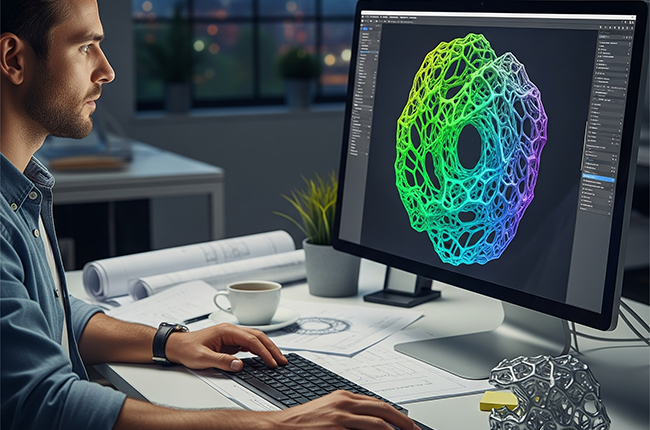

Generative design has several key benefits that make it a game-changer in engineering:
Speed and Efficiency – Traditional design processes can take weeks or months, but generative design can deliver hundreds of options in a fraction of the time. This faster process means products reach the market more quickly.
Innovation and Creativity – With generative design, engineers are no longer limited to familiar shapes and structures. The software explores innovative forms that can be lighter, stronger, or use less material, leading to more creative and efficient designs.
Reduced Waste – By optimizing designs for material efficiency, generative design helps reduce waste. This is especially important in industries where materials are costly or environmental impact is a concern.
Cost Savings – Generative design can reduce production costs by minimizing the amount of material used and by helping engineers choose cost-effective manufacturing methods.
Real-World Applications of Generative Design
Generative design is already making waves in several industries. Here are some examples:
Aerospace – Weight reduction is critical in aerospace, and generative design helps create lightweight yet strong parts for aircraft and spacecraft. For instance, Airbus used generative design to develop a partition for their aircraft that was both strong and 45% lighter than previous designs, resulting in fuel savings and a lower carbon footprint.
Automotive – Automakers use generative design to develop parts that are both lighter and stronger, which improves fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. For example, General Motors used generative design to create a new seat bracket that combined multiple parts into one, making it 40% lighter and 20% stronger.
Consumer Products – Companies designing furniture, sports equipment, and electronic gadgets use generative design to make products that are more stylish, lighter, and cost-effective. This approach enables them to bring unique products to market that stand out from the competition.
Construction – Generative design helps architects and engineers design buildings that use less materials and are more sustainable. By optimizing structures for strength and resource efficiency, the construction industry can reduce costs and environmental impact.
Challenges and the Future of Generative Design
As promising as generative design is, it still has some challenges. One is the need for high computing power. Processing so many design options require powerful computers, which can be costly. Another challenge is the learning curve—engineers need training to understand and effectively use generative design software.
However, as technology advances, these challenges are gradually being addressed. Cloud computing, for example, makes it easier to access the computing power needed for generative design. And with more user-friendly software being developed, generative design is becoming accessible to a wider audience.
A New Era in Engineering
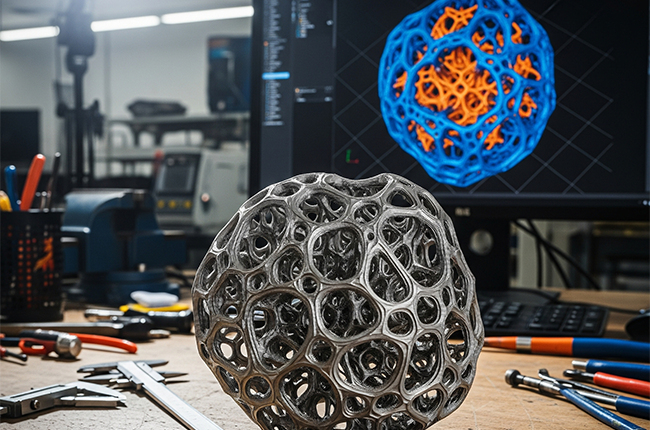
Generative design is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in engineering. It’s no longer just a tool but a collaborator, one that can help engineers and designers explore new ideas, save costs, and reduce environmental impact. As more companies adopt this technology, we’re likely to see more innovative products and smarter, more efficient manufacturing processes.
Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, construction, or consumer products, generative design opens exciting possibilities. By combining human creativity with the power of AI, generative design is indeed shaping the future of engineering, making it faster, smarter, and more sustainable.