A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Sheet Metal: Properties, Uses, and Applications

Sheet metal is everywhere, even if we don't always notice it. From the cars we drive to the appliances in our homes, sheet metal plays a huge role in modern life. But what exactly is sheet metal? What makes it worthwhile, and why is it used in many industries? Let's break it down in simple terms so you can understand its properties, uses, and the wide variety of applications it has.
What is Sheet Metal?
Sheet metal is simply metal rolled out into thin, flat pieces. Think of it like rolling out dough to make pizza—except instead of dough, we're working with metal. The thickness of sheet metal can vary a lot, from very thin sheets (like foil) to much thicker ones used in heavy-duty applications. Usually, the thicker the sheet, the stronger it is.
Sheet metal is typically made from materials like:
Steel: The most common type, known for its strength and durability.
Mild steel(CR/HR). - hot role use for a structural eng, and skeleton for a any appliance/cold role from .5 mm to 3MM for a lighter application.
Stainless Steel: In SS 304 grade, 316 grade used in different application, rust proof, and long lasting ,material used in medical, aerospace, all transportation vehicle.
Aluminium is light and corrosion-resistant, making it great for outdoor use.
Copper: Known for its excellent electrical conductivity, it is often used in wiring and electrical parts.
Brass: A mixture of copper and zinc, brass is used for its decorative properties and corrosion resistance.
Titanium: Strong and lightweight, titanium is often used in high-tech industries like aerospace.
Combination of above material used for a special application for strength and durability.
Properties of Sheet Metal
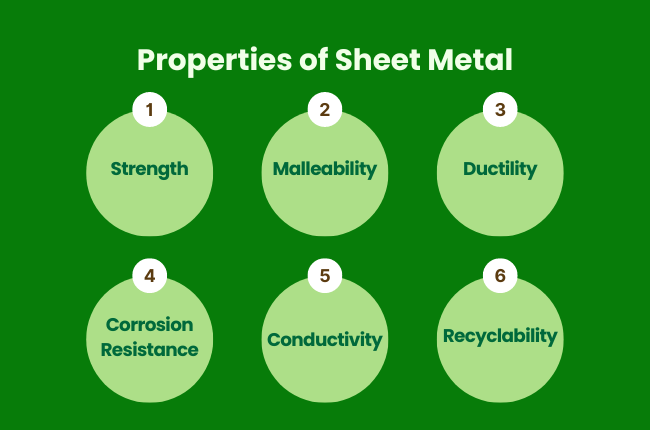
So, what makes sheet metal unique? Here are some fundamental properties:
Strength: Sheet metal is vital, specially made of steel. It can withstand a lot of pressure and force without breaking.
Malleability: This means it can be bent or shaped easily. That's important because it allows manufacturers to form sheet metal into different shapes without cracking.
Ductility: Sheet metal can be stretched into thin wires without breaking, which makes it useful for electrical applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Certain metals, like aluminium and stainless steel, resist rust and corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor use or in environments where moisture is a concern.
Conductivity: Metals like copper are excellent conductors of electricity and heat, which is why sheet metal is used in electrical applications.
Recyclability: Metal is generally highly recyclable, and sheet metal is no exception. It can be melted down and reused, making it an environmentally friendly material.
Common Uses of Sheet Metal
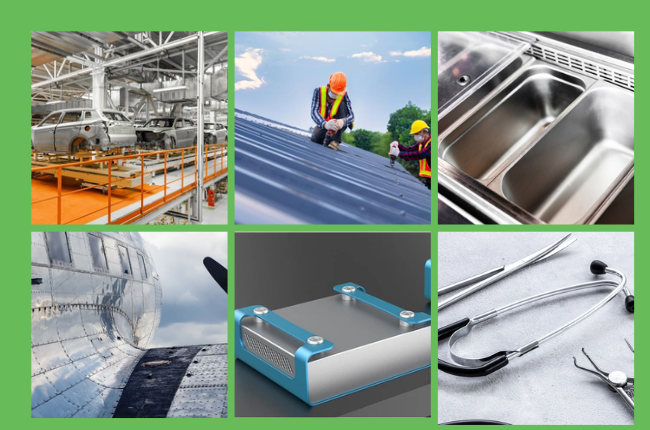

Sheet metal is incredibly versatile so that you can find it in many everyday items. Here are some of its most common uses:
Automotive Industry: The automotive industry is one of the biggest users of sheet metal. Sheet metal is used to make car bodies, chassis, and other components because it's strong and can be easily shaped into different forms.
Construction: Sheet metal is used for roofing, siding, and even structural components in buildings. Its ability to withstand the elements and durability make it ideal for construction projects.
Appliances: Your refrigerator, washing machine, and oven probably all have sheet metal. Sheet metal is durable and easy to clean, making it perfect for appliances.
Aerospace: Sheet metal, especially lightweight materials like aluminium and titanium, is also used in aeroplanes. These metals help reduce the aircraft's weight while maintaining strength, which is crucial for safety and fuel efficiency.
Electronics: Copper and other conductive metals are often used as wiring and components in electronic devices. Sheet metal's malleability makes it easy to form intricate shapes for circuit boards and other parts.
Medical Equipment: Stainless steel sheet metal is often used in medical devices and hospital equipment because it's easy to sterilize and resists corrosion.
Applications of Sheet Metal Across Industries
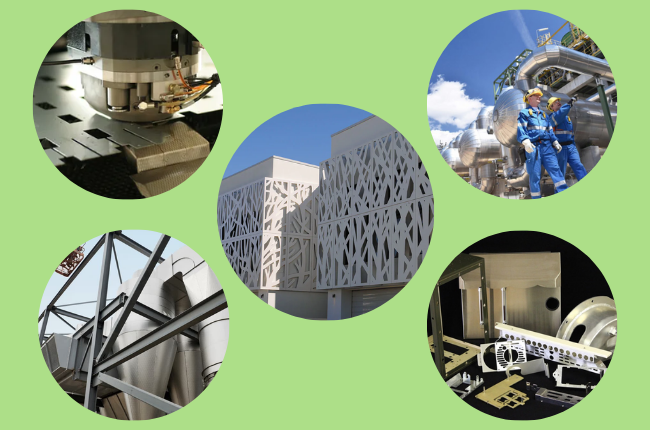

Sheet metal isn't just limited to one or two industries; it's used across various fields. Let's explore some of these:
Manufacturing and Prototyping
Sheet metal is essential in the world of manufacturing. It's used to make everything from small brackets to large enclosures. Its malleability allows manufacturers to create custom parts for machinery or consumer goods.
Sheet metal can be quickly shaped into a model for testing in prototyping. Once the prototype is approved, it can be mass-produced efficiently.
Architectural Designs
Sheet metal isn't just functional—it can be beautiful, too. Architects use it for decorative purposes, such as in cladding and facades. Metal adds a sleek, modern look to buildings and can be treated with various finishes, like brushed or polished surfaces.
Energy Sector
Sheet metal is used in the energy industry, especially in renewable energy systems like solar panels. Aluminium and steel are commonly used for mounting systems and frames due to their durability and resistance to corrosion.
Oil and Gas Industry
In oil and gas, sheet metal creates pipelines, storage tanks, and other essential equipment. The material's ability to withstand extreme conditions is critical in this industry.
Consumer Goods
Even everyday items like kitchen utensils, electronics casings, and decorative pieces often feature sheet metal. Its versatility makes it a go-to material for both function and style.
Final Thoughts!
Sheet metal may seem like a simple material, but it's one of the world's most versatile and widely used materials today. Its strength, flexibility, and durability make it the go-to choice for industries ranging from construction and automotive to aerospace and electronics. Whether protecting a building from the elements, helping a car stay lightweight yet strong, or making the devices we use daily, sheet metal is at the heart of many essential applications.
The next time you see a car, walk into a building or use an appliance, you'll better understand sheet metal's role in making it all possible.