4 Common Techniques Used in the Metal Laser Cutting Industry
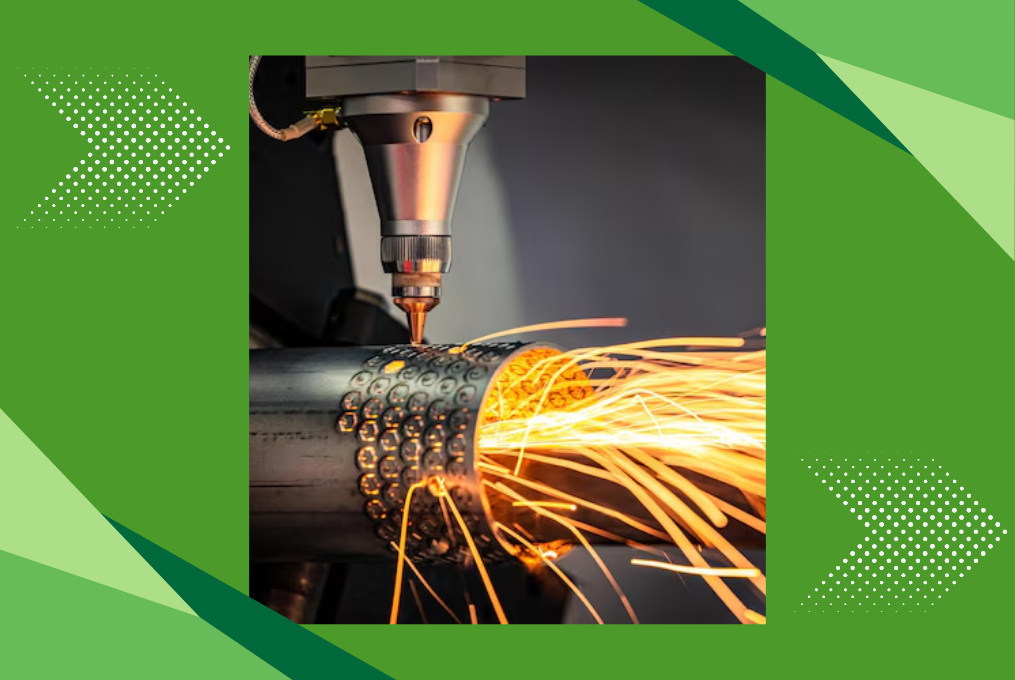

Laser cutting is one of the most important technologies used in metalworking today. It’s quick, accurate, and can handle a wide variety of materials. If you've ever wondered how industries cut metal into specific shapes with such precision, laser cutting is often the answer. Whether it’s for small electronics or huge construction projects, metal laser cutting has made things much easier and more efficient. In this blog, we’ll learn four common techniques used in the metal laser cutting industry. Don’t worry – we’ll keep things simple and easy to understand!
Fusion Cutting
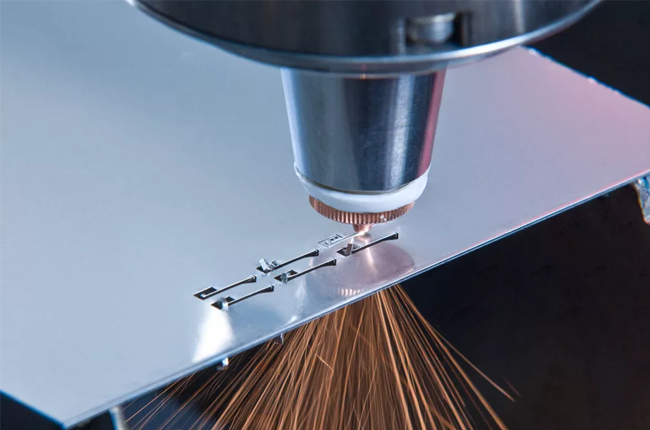

Fusion cutting is probably the most common type of laser cutting you’ll come across in the industry. It works by melting the metal with a laser beam, then using a gas, like nitrogen, to blow the molten material away. This creates clean and smooth edges, which is why it’s often used for cutting materials like stainless steel and aluminum.
Here’s why fusion cutting is so popular:
Precision: It allows for highly detailed and accurate cuts, even on thick materials.
No oxidation: Since nitrogen is used instead of oxygen, the cut surface doesn’t rust or oxidize, making it perfect for industries where the appearance of the metal matters, like in automotive or aerospace.
While it’s one of the most common techniques, fusion cutting does require a high-power laser and is usually used for metals that are more sensitive to oxidation.
Flame Cutting
Flame cutting is another method widely used in metal laser cutting, especially for thicker and harder metals. In this technique, a laser is used to heat the metal to a very high temperature. Once its heated, oxygen is blown over the surface, which reacts with the metal to form an oxide. This process creates heat, which helps cut through the material even faster.
Why choose flame cutting?
Best for thick metals: Flame cutting works really well for cutting through thicker metals like steel.
Cost-effective: It’s generally more affordable than other methods because the equipment needed isn’t as expensive, and oxygen is cheap.
On the flip side, flame cutting is not as precise as fusion cutting. You might notice rougher edges, and the metal can oxidize, which is a downside if the metal needs to be polished or aesthetically pleasing.
Vaporization Cutting
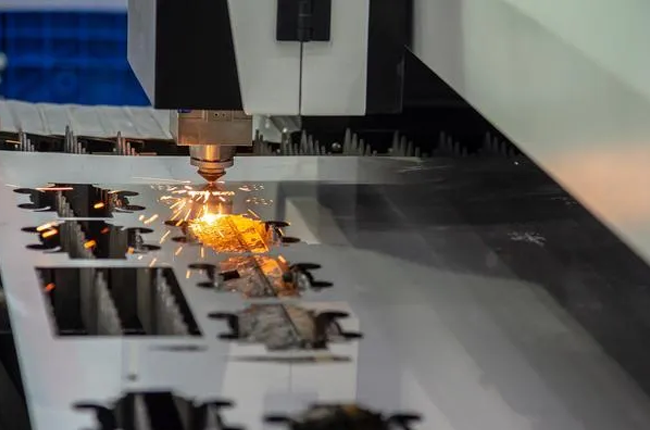
This method is a bit different from the previous two. Instead of melting the metal, vaporization cutting uses a laser to heat the metal to a point where it turns directly from a solid to a gas, leaving no molten material behind. The gas is then blown away, leaving behind a clean cut. This technique is often used for materials like wood and plastic, but it also works with metals, especially thin sheets.
What makes vaporization cutting unique?
Extremely precise: Since no molten material is involved, you get incredibly clean cuts, which is great for detailed work.
Perfect for thin materials: If you’re working with thin sheets of metal, this method can give you a very fine, sharp edge.
However, vaporization cutting isn’t as widely used for metal as other methods because it requires a lot of laser power, making it less energy-efficient and more expensive for thicker materials.
Laser Drilling
You might not think of drilling when you hear about cutting, but laser drilling is actually a crucial technique in the metalworking industry. It’s exactly what it sounds like – using a laser to drill holes in metal. The laser beam focuses on a specific point, and the heat from the laser vaporizes or melts the metal at that spot, creating a hole.
Here’s why laser drilling is so useful:
Precision: Laser drilling can create tiny holes with extreme accuracy, which is hard to achieve with traditional drilling tools.
No contact: Since the laser never actually touches the metal, there’s no wear and tear on tools, meaning less maintenance.
Laser drilling is often used in industries like aerospace and electronics, where very small, precise holes are needed for components like engine parts or circuit boards. It’s also used for perforating metal sheets, where multiple small holes are needed.
Final Thoughts!
Metal laser cutting has completely transformed the way industries work with metal. Whether you need a smooth finish, high precision, or the ability to cut through thick materials, laser cutting has a solution. The four techniques we’ve discussed – fusion cutting, flame cutting, vaporization cutting, and laser drilling – each have their own strengths, making them suitable for different kinds of projects.
The next time you see a complex metal part or structure, there’s a good chance laser cutting played a role in creating it. With the growing demand for faster and more efficient manufacturing, the use of these techniques is only going to increase, shaping the future of metalworking.
Hopefully, this blog has given you a better understanding of the different techniques used in the metal laser cutting industry – without the technical jargon!